Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number
Elements in the periodic table are arranged by increasing atomic number
Distinguish between the terms group and period
Apply the relationship between the electron arrangement of elements and their position in the periodic table up to Z=20
Apply the relationship between the number of electrons in the highest occupied energy level for an element and its position in the periodic table
Period- A horizontal row of elements on the periodic table
The period number gives the number of the highest occupied energy level
Group- A vertical column of elements on the periodic table
The group number gives the number of valence electrons in the outermost energy level
Define the terms first ionization energy and electronegativity
First Ionization energy- The amount of energy (in kJ) needed to remove the outermost valence electron
Electronegativity- The relative ability of an element to attract valence electrons
Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies, electronegativities, and melting points for the alkali metals (Li à Cs)and the Halogens
Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies, and electronegativities for elements across period 3.
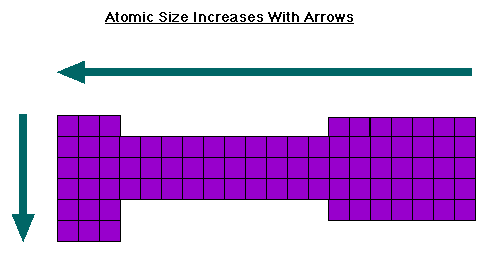
Atomic Radius
Atomic Radius- Distance from the nucleus to the outermost valence electron
The trend of the atomic size across the periodic table- Increases across the period and increases down the group:
Why does the trend appear this way?
As one moves across the period, the number of atoms in the nucleus increases while the number of electrons between the valence shell and the nucleus (i.e. the electron screen or shield) that repel the valence electrons stays the same. Since the force of attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons is stronger, the valence electrons will be pulled closer to the nucleus and the atomic radius will decrease.
As one moves down a group, additional valence levels are added farther and farther from the nucleus. Since there are more shells of shielding electrons repelling the valence electrons, there will be a larger atomic size.
Ionic Radius
Ionic Radius- Distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron of an ion
The radius of a cation is smaller than the radius of a neutral atom, because there is the same number of protons pulling on a fewer number of electrons, so the force of attraction per electron is greater and valence electrons are pulled in closer.
The radius of an anion is larger than the radius of a neutral atom, because there is the same number of protons pulling on a greater number of electrons, so the force of attraction per electron is less and the valence electrons are not pulled in as closely
Isoelectronic Series- a series of different elements with the same number of electrons. The most positive compounds will have the smallest ionic radii
First Ionization Energy
Trend of first ionization energy across the periodic table- As one moves across a period, first ionization energy gets stronger. As one moves down a period, first ionization energy gets weaker.
Why does the trend appear this way?
As you move across a table, the nucleus pulls on each valence electron with a greater amount of force due to less electron shielding from the non-valence (core) electrons. Because of this greater force of attraction, it will take more energy to remove the outermost valence electron.
As you move down a group, the nucleus pulls on each valence electron with less force because there is more shielding from the inner-core electrons. Since the nucleus is pulling on each electron with less force, it will not take as much energy to remove the outermost valence electron.
*NOTE: Recognize the trends in First Ionization Energy and Atomic Size are the exact opposite
Electronegativity
Trend in electronegativity- Same as trend in first ionization energy for the same reasons
Melting and Boiling Points
Discuss the similarities and differences in the chemical properties of elements within the
same group
Alkali + Water produce a violent reaction (2Na + H2O à Na2O + H2)
Alkali + Halogen produce salt under high temperature (2Na + Cl2 à 2NaCl)
Halogen + Water produce acids (Cl2 + H2O à HCl + HClO)
At room temperature: Flourine is a pale yellow gas, Chlorine is a yellow green gas, bromine is a reddish-brown liquid, and Iodine is a solid that turns into black and purple vapor when heated
Reactivity- Decreases as you go down a group because electrons are further from the nucleus and new electrons are not taken as easily.
In an ionic solution, the more reactive halogens will substitute the less reactive halogen
Example: F2(g) + 2Cl- (aq) à 2F- (aq) + Cl2 (g) POSSIBLE!!
Example: Br2(aq) + 2Cl- (aq) –Xà 2Br- + Cl2 (g) IMPOSSIBLE!!!
HALOGEN TABLE OF DOOM
F- | Cl- | Br- | I- | |
Aqueous Ag+ | N/A | White precipitate. Black in sunlight | Cream precipitate | Pale yellow precipitate |
Chlorine | N/A | N/A | Yellow then brown solution | Yellow then black precipitate |
Bromine | N/A | N/A | N/A | Yellow then black precipitate |
Iodine | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Discuss the changes in nature from ionic to covalent and from basic to acidic of the oxides across Period 3
the resulting solution becomes acidic because the Period 3 elements bind with the OH- (or O2-), leaving spare H+ ions in the solution.
What does increasing hydrolysis mean? Reactivity of a substance as it is dissolved when placed in water
When ionic compounds (Na/Mg) are dissolved in water- it remains neutral because it dissolves without hydrolyzing the water.




This work is worth it...thanx.
ReplyDeleteThank you for sharing such helpful information with us. Students who are interested in taking the best home tuition for class 10 can register with Ziyyara by filling in all the required details.
ReplyDelete